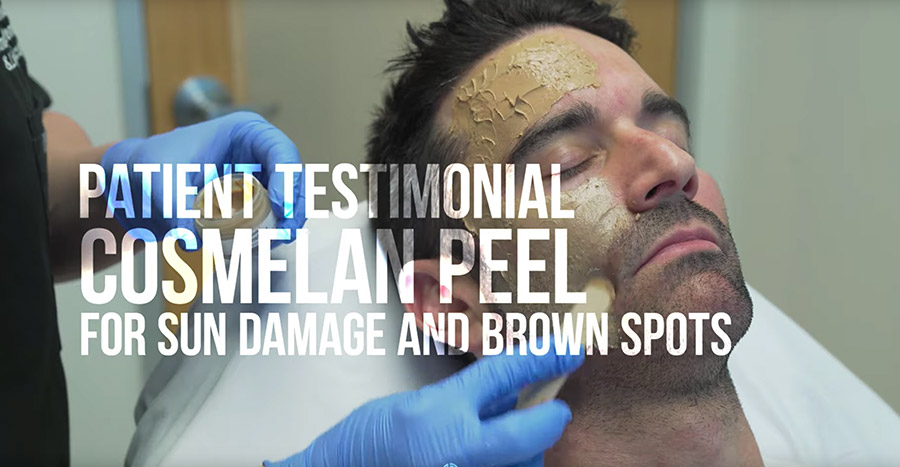
Melasma is a type of hyperpigmentation that appears as brown or grayish patches on the face, often symmetrical and affecting areas like the cheeks, forehead, bridge of the nose, and upper lip. It is more common in women, especially those with darker skin tones, and can worsen with hormonal changes like pregnancy or birth control pills.
Causes: The exact cause of melasma is unknown, but several factors are believed to contribute, including:
- Sun exposure: Sun exposure is a major trigger for melasma, stimulating melanin production and worsening discoloration.
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in hormones, such as during pregnancy or with birth control use, can contribute to melasma.
- Genetics: People with a family history of melasma are more likely to develop it.
Treatments: Melasma can be stubborn and difficult to treat. A combination approach often yields the best results. Sun protection is paramount. Topical creams containing ingredients like hydroquinone, kojic acid, azelaic acid, or retinoids may be prescribed by a dermatologist. Chemical peels, laser therapy, and microneedling may also be offered for more resistant cases.
Disclaimer: Completely clearing melasma can be challenging, and it may recur with sun exposure or hormonal changes. Consistent sun protection, a dermatologist-guided treatment plan, and managing triggers are crucial for managing melasma.