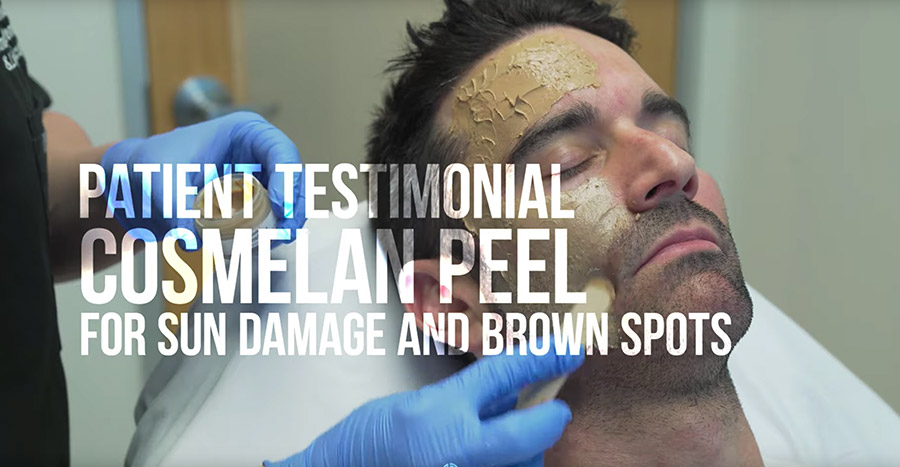
Sun damage refers to the visible and cellular changes in the skin caused by excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. These changes can manifest in various ways, including:
- Sunburn: Redness, pain, and inflammation of the skin after overexposure to UV rays.
- Tanning: Increased skin pigmentation as a protective response to UV radiation.
- Premature aging: Wrinkles, fine lines, and loss of skin elasticity.
- Age spots: Flat, brown spots on sun-exposed areas.
- Increased risk of skin cancer: Chronic sun exposure is a major risk factor for various skin cancers.
Treatments: While some of the visible signs of sun damage, like tanning, fade over time, others may be permanent. Treatments like topical retinoids, chemical peels, and laser therapy can help improve the appearance of sun damage. However, the most important strategy is prevention through consistent sun protection with SPF 30 or higher and broad-spectrum UVA/UVB protection.
Disclaimer: Completely reversing sun damage might not always be possible. Sun protection is crucial to prevent further damage and minimize the risk of skin cancer.